Focus
Accounting for differences between reality and perceptions of realityPrincipal Metaphors
- Knowledge is … external reality
- Knowing is … internal interpretations
- Learner is … an individual mind (insulted and isolated from the world)
- Learning is … interpreting
- Teaching is … conveying and testing
Originated
1600s (formally developed in the 1970s)Synopsis
Critical Realism was articulated centuries ago as a response to Realism (a.k.a. Naive Realism). In Roy Bhaskar’s (1970s) account, Critical Realism is understood through two dimension:- Intransitive Dimension – real, mind-independent objects, structures, and mechanisms that exist regardless of whether humans perceive or understand them, including natural laws, causal powers, and phenomena (e.g., gravity)
- Transitive Dimension – theories, models, concepts, and methods that humans create to understand the Intransitive Dimension. This dimension is shaped by social, historical, and cultural contexts and is constantly evolving.
- Primary Qualities – observer-independent, objectively measurable aspects of a form or event
- Secondary Qualities – observer sensations, subjectively determined aspects of a form or event
- Anti-Realism (Michael Dummett; 1960s) – As the name suggests, Anti-Realism begins by rejecting the “realist” assumption that truths are literal depictions of an external, independent reality. Within Antirealism, the truth of an assertion is determined through internal logic mechanisms. (Notably, some of those mechanisms vary considerably from the tenets and constraints of classical logic.)
- Transformational Model of Social Activity (TMSA) (Roy Bhaskar, 1970s) – a perspective on the dynamic interaction between human agency and social structures. TMSA asserts that society shapes individuals, but individuals simultaneously reproduce or transform societal structures through their actions over time.
Commentary
An obvious problem with Critical Realism, on top of the cluster of issues typical of most Correspondence Discourses, is that the separation of Primary Qualities from Secondary Qualities is entirely problematical. As some commentators have highlighted, tools for “objective” measurement are created by humans who, according to the theory, are prone to conflating Primary Qualities and Secondary Qualities – meaning that those tools could be (and likely are) fundamentally flawed. The perspective very quickly dissolves into a forced acknowledgement that human objectivity must be a matter of social agreement rather than external truth.Authors and/or Prominent Influences
John Locke; Roy BhaskarStatus as a Theory of Learning
Critical Realism is normally classified as a philosophy or worldview, but it can be seen as a theory of learning because it has clear and immediate entailments for how one comes to know – namely, taking in a world through the senses.Status as a Theory of Teaching
Critical Realism is not a theory of teaching, but its core distinction between primary and secondary qualities persists as a popular explanatory principle in traditional teaching practices. It is especially prominent in justifications for continuous testing (i.e., used to ensure subjective interpretations match with objective reality).Status as a Scientific Theory
Critical Realism is the opposite of a scientific theory – although, not without irony, it was a dominant sensibility in the early stages of the Scientific Revolution.Subdiscourses:
- Anti-Realism
- Intransitive Dimension
- Primary Qualities
- Secondary Qualities
- Transformational Model of Social Activity (TMSA)
- Transitive Dimension
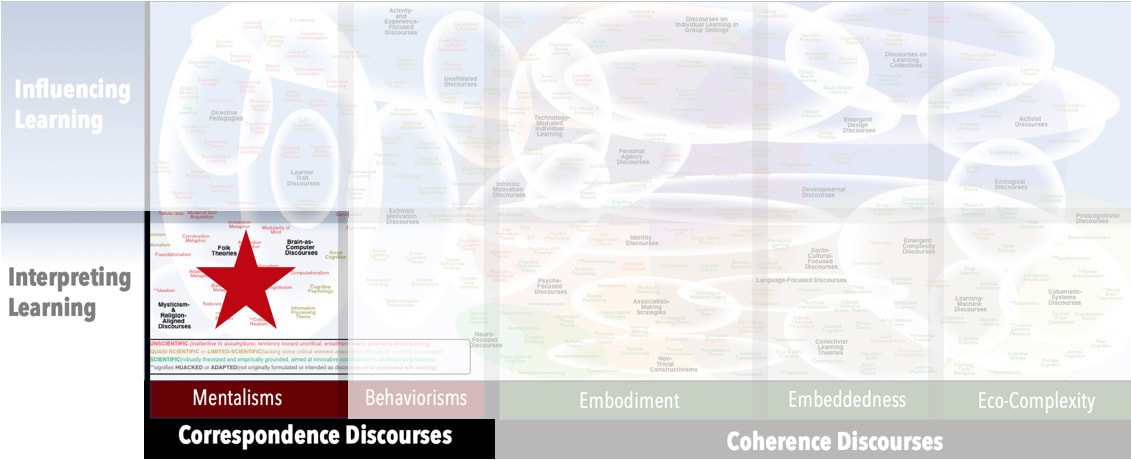
Map Location
Please cite this article as:
Davis, B., & Francis, K. (2025). “Critical Realism” in Discourses on Learning in Education. https://learningdiscourses.com.
⇦ Back to Map
⇦ Back to List
