Focus
Applying insights into the structure and dynamics of the nervous systemPrincipal Metaphors
- Knowledge is … dynamic networks
- Knowing is … situation-appropriate responses
- Learner is … a nervous system
- Learning is … iterative restructuring
- Teaching is … triggering
Originated
late-1900sSynopsis
The 1990s saw an explosion of publications out of Neuroscience and Cognitive Science that were aimed at popular audiences. Almost overnight, it seemed, thinking about the brains in terms of containers or computers gave way to notions of vibrant complex systems that arise in, are coupled to, and are elements of many and varied other complex forms. By 2000, many educators and educational researchers were signaling how this shift in thinking undermined prevailing sensibilities on learning, intelligence, identity – sensibilities that infused or oriented much of schooling practice. Since then, researchers have been seeking to understand educational implications of the brain’s networked structure, its lifelong plasticity, and many other emergent insights … all with, disappointingly, little obvious impact on entrenched schooling practices.The Brain
Because the brain features more and more prominently in the educational literature, we highlight below some of the more commonly mentioned elements, regions, and associated constructs:
- Nervous System – the network of cells, tissues, and organs that sense and interpret information, coordinate the body’s voluntary and involuntary movements, and regulate the body’s functions (e.g., digestion, respiration, blood circulation) in response to any psychological, social, or environmental trigger
- Structurally, the Nervous System is seen to comprise two major aspects:
- Central Nervous System – the brain and spinal cord, responsible for connecting sensations and perceptions with actions
- Peripheral Nervous System – a messenger system comprising a web of cells that carry information to and from the Central Nervous System to other parts of the body
- The Nervous System is seen to have two major functional subdivisions:
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS) – the aspects of the Nervous System that control voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The
Somatic Nervous System is associated with three interconnected networks, each with a distinct function:
- Central Executive Network (CEN; Executive Control Network; ECN) – the brain network that governs high-level cognitive functions like decision-making, problem-solving, working memory, and attention. It is responsible for externally focused, goal-driven tasks requiring active engagement.
- Default Mode Network (DMN) – the brain network that engages during internally focused activities such as daydreaming, self-referential thinking, memory retrieval, and imagining the future. It is also associated with feats of imagination and creativity, as well as with feelings of compassion, gratitude, and awe.
- Salience Network (Salience Emotion Network; SEN; SN) – a mediator between the DMN and CEN, determining which network is most appropriate to activate based on current demands
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) – the aspects of the Nervous System that regulate involuntary physiological processes. The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) has two subsystems, each with a distinct function:
- Sympathetic Nervous System – those aspects of the Somatic Nervous System that are mobilized to respond to threats (See Motivation Theories for some prominent associated discourses on learning.) Associated phenomena include:
- Sympathetic State (Hyperarousal) – a state of heightened arousal (that may trigger Fight, Flight, or Freeze responses; see Drives, Needs, & Desires Theories) that is triggered when the Sympathetic Nervous System is activated by a perceived threat or stress
- Parasympathetic Nervous System – those aspects of the Somatic Nervous System that are associated with establishing and maintaining states of calm (See Well-Being Discourses for some prominent associated discourse on learning.) Associated phenomena include:
- Parasympathetic State (Rest and Digest) – a state of calmness or relaxation associated with the activation of the Parasympathetic Nervous System. (The alternative name, Rest and Digest, is offered in contract to Fight or Flight activations associated with the Sympathetic Nervous System, mentioned above.)
- Vagus Nerve – the primary conduit for the Parasympathetic Nervous System. Key associated structured include:
- Dorsal Vagal Complex (Primitive Vagal System) – a structure in the Medulla Oblongata that contributes to the function of the Vagus Nerve, playing a critical role in regulating autonomic functions such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory processes
- Ventral Vagal Complex (Social Vagal System) – part of the Vagus Nerve’s circuitry, playing a central role in regulating social behavior, emotional engagement, and calming physiological states
- Nervous System Dysregulation (Dysregulated Nervous System) – an imbalance of the Sympathetic Nervous System and the Parasympathetic Nervous System, typically manifesting as a psychological problem or a mental illness (See Psychotherapy – especially the subsection, “Psychotherapies with holist sensibilities” – for some prominent associated discourses on learning.)
- Sympathetic Nervous System – those aspects of the Somatic Nervous System that are mobilized to respond to threats (See Motivation Theories for some prominent associated discourses on learning.) Associated phenomena include:
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS) – the aspects of the Nervous System that control voluntary movements of skeletal muscles. The
- Structurally, the Nervous System is seen to comprise two major aspects:
The brain has three basic compositional elements:
- Neurons (Nerve Cells) – comprising about 10% of the Nervous System, specialized cells that transmit information through electrical and chemical signals. Types include:
- Sensory Neurons – neurons associated with sensory systems that are activated by (i.e., detect) and transmit information
- Interneurons (Relay Neurons) – neurons that integrate and interpret information from Sensory Neurons
- Motor Neurons – neurons that distribute information across the body about responses and behaviors
- Synapses – tiny gaps between the branches of Neurons, across which information passes via Neurotransmitters
- Neurotransmitters – a variety of chemicals that enable communication among neurons by traveling between Synapses. Types include:
- Acetylcholine – a Neurotransmitter associated with muscle activation, attention, and memory
- Dopamine – a Neurotransmitter that plays key roles in triggering and amplifying desire, and so has been associated with how one feels pleasure, experiences reward, learns, remembers, maintains motivation, and regulates mood. Dopamine has garnered much attention in the popular educational literature, evident in such constructs as:
- Addictive Learning (2010s) – a positive term referring to learning experiences that are engaging, rewarding, and immersive – that is, highly motivating and enjoyable, and thus often associated with Dopamine release
- Dopamine Addiction (Dopamine Dependency; Dopaminergic Addiction; Neurochemical Addiction) – a behavioral pattern where a person becomes overly reliant on activities or substances that trigger excessive Dopamine release in the brain
- Dopamine Detox (Dopamine Fasting) – taking a break (of hours to days) from activities that provide instant gratification – i.e., those activities that are popularly associated with “dopamine hits.” The goal is to reduce the frequent and artificial spikes in Dopamine that can lead to cravings, distraction, and a lack of motivation for more productive tasks. Related constructs include:
- Digital Detox – a type of Dopamine Detox that refers specifically to taking a break from using digital devices (especially for accessing social media) with the intention of reducing stress, improving in-person relationships, and diversifying physical activities
- Treat Brain (Imogen West-Knights, 2020s) – a state of mind characterized by impulsive behaviors to seek immediate gratification, such as making quick purchases. This behavior is linked to the brain’s pursuit of Dopamine.
- Endorphins – Neurotransmitters associated with sensations along the distress–pleasure continuum – including, e.g., moderating feelings of physical and emotional pain, sense of well-being, happiness, and euphoria
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline) – a Neurotransmitter involved associated with arousal, energy, stimulation, and concentration
- GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) – a Neurotransmitter associated with calmness and relaxation, operating by slowing brain function and blocking specific signals
- Glutamate – an excitatory Neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory
- Histamine – a Neurotransmitter involved in immune response (especially mediating allergic reactions), regulating sleep-wake cycles, and digestion
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline) – a Neurotransmitter involved in arousal, alertness, and the fight-or-flight response, operating by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and blood flow to muscles
- Oxytocin – a Neurotransmitter associated with social bonding and trust
- Serotonin – a Neurotransmitter associated with emotional stability, self-regulation, self-confidence, sleep, and appetite
- Neurotransmitters – a variety of chemicals that enable communication among neurons by traveling between Synapses. Types include:
- Glial Cells (Neuroglia) – comprising about 90% of the Nervous System, specialized cells that, among other functions, afford structure to hold Neurons in place and to supply them with Neurotransmitters
Many brain regions have been identified. Below we have list parts that are mentioned with some frequency in the educational literature. Note that there is considerable overlap in functionality across parts, underscoring that few capabilities are entirely located in or determined by specific brain regions.
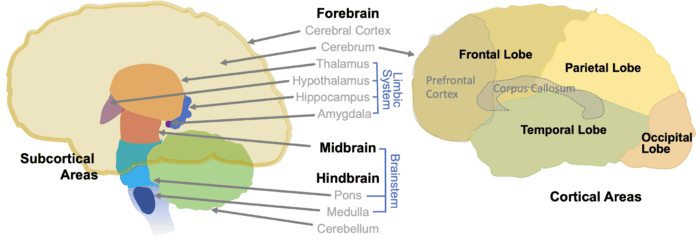
- Forebrain (Prosencephalon) – the major part of the human brain, playing the principal role in perception, thinking, languaging, and motor function. The Forebrain was the last part of the brain to evolve and is the last to develop in a fetus. Major components include:
- Cerebral Cortex (Cortex) – a thin outer layer covering the Cerebrum, associated with a range of higher-level capacities, including language, reasoning, decision-making, creativity, intelligence, and personality
- Cerebrum – the largest part of the brain, regarded as the controller and/or locus of thought, speech (and other language capacities), and learning
- Hemispheres
- Right Hemisphere – a region attentive to relationships and holistic understandings, tending to interpret all forms as alive and co-entangled
- Left Hemisphere – a region that tends to parse elements of perception and to interpret them in terms of mechanical interactions
- Cortical Areas – brain areas involving the four lobes of the Cerebrum
- Frontal Lobes – the largest lobes, associated with executive control, including managing thought, judgment, emotions, personality, muscle control, and memory. Components include:
- Prefrontal Cortex (PFC) – the foremost part of the Frontal Lobes, playing major roles in decision making, personality, consciousness, executive functioning, and social behavior
- Occipital Lobes – located at the back of the brain, associated with spatial and visual competencies, including identifying color, discerning shapes, tracking movement, and locating objects
- Parietal Lobes – located in the upper back of the brain, associated with interpretation so f sensory information and focusing attention
- Temporal Lobes – located behind the ears, associated with interpreting and remembering auditory information, producing speech, and making sense of visual stimuli
- Frontal Lobes – the largest lobes, associated with executive control, including managing thought, judgment, emotions, personality, muscle control, and memory. Components include:
- Hemispheres
- Corpus Callosum (Callosal Commissure) – a thick bundle of nerve cells located between the two Hemispheres that both mediates communication between them and enforces hemispheric independence
- Limbic System (Emotional Brain) – a complex set of structures that plays a key role in regulating emotions, behavior, memory, and physiological responses. Its key components include:
- Amygdala – a small region that is involved in processing emotions such as fear, anger, and pleasure. It plays a role in recognizing emotional cues and forming emotional memories.
- Hippocampus – a region behind the Thalamus that is essential for learning and memory, particularly converting short-term memories into long-term ones. It also plays a role in spatial navigation.
- Hypothalamus – a small region that plays a key role in regulating and balancing multiple body functions (e.g., body temperature, emotional responses, appetite, sexual behavior, circadian rhythms)
- Thalamus – the brain’s information relay center, through which all bodily sensations (expect smell) pass. The Thalamus also participates in sleep, awareness, learning, and memory.
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon) – a relatively small part of the brain that is associated with perception (especially hearing and vision), arousal (alertness and wakefulness), motor control, and other functions associated with coupling with the world. The Midbrain was the second part of the brain to evolve and is the second to develop in a fetus. Major components include:
- Reticular Formation (Reticular Activating System) – a key system in enabling attention and supporting consciousness, among other functions
- Hindbrain (Lower Brain; Rhombencephalon) – the parts of the brain located where the spinal cord enters. The Hindbrain was the first part of the brain to evolve and is the first to develop in a fetus. Major components include:
- Cerebellum – the part of the brain that detects movement and shifts in balance, and so plays important roles in coordination of muscles and learning of motor actions
- Medulla (Medulla Oblongata) – the part of the brain that regulates heart function, respiration, blood pressure, and several reflexes (such as swallowing and coughing)
- Pons – the part of the brain that manages several unconscious processes, including the sleep–wake cycle and many facial movements
- Sensory System – a specialized part of the human body that detects, interprets, and responds to specific types of external or internal stimuli. Each sensory system includes dedicated sensory receptors and neural pathways and is associated with specific regions or networks in the brain that interpret the resulting signals. The question of how many sensory systems humans have is more complex than is often acknowledged. There is consensus on the traditional “five senses”:
- Hearing (Auditory System) – perception of sound through vibrations detected by the ears
- Sight (Vision; Visual System) – ability to detect light, color, and shapes through receptors in the eyes
- Smell (Olfactory System) – detection of airborne chemicals by receptors in the nose
- Taste (Gustatory System) – detection of flavors via taste buds on the tongue (sweet, salty, sour, bitter, umami)
- Touch (Tactile System) – broad sense involving receptors in the skin for pressure, temperature, and pain
- Beyond these core five senses, there is broad – but not universal – agreement on the existence of the following sensory systems:
- Nociception (Pain Sense) – perception of pain (sometimes considered an element of Touch)
- Proprioception – sense of body position and movement, informed by receptors in muscles, tendons, and joints
- Thermoception – ability to detect temperature changes, both in the environment and in one’s own body
- Vestibular System (Balance System; Equilibrioception) – sense of spatial orientation and balance, located in the inner ear
- Visceroception – sense the internal organs and bodily states, such as heart rate, hunger, thirst, and digestion
- Additional senses have been hypothesized or are under research, though they are less widely accepted or understood. These include:
- Blood Glucose Sensing – speculated capacity to be aware of blood sugar levels
- Chemoreception Beyond Smell and Taste – speculated to be a subtle capacity to detect chemicals that aren’t consciously perceived as taste or smell, but that can still influence mood or behavior (e.g., pheromone detection)
- Chronoception (Time Perception) – speculated to be a sense of the passing of time
- Electroreception – speculated to be a subtle capacity to detect electric fields
- Infrared Detection (Heat Sense) – speculated ability to detect infrared radiation, similar to snakes
- Magnetoreception – speculated to be a subtle, largely unconscious ability to detect magnetic fields
- Brainwaves – rhythmic patterns of electrical activity in the brain. Different frequencies are associated with various mental states, levels of consciousness, and functions. Primary types (listed in order of increasing frequency) include:
- Delta Waves – low frequency (0.5–4 cycles/second) Brainwaves that are dominant during deep, dreamless sleep. They are associated with healing, immune function, and brain recovery.
- Theta Waves – low frequency (4–8 cycles/second) Brainwaves that often occur in the early stages of sleep or in states of relaxation. They are associated with memory, imagination, creativity, and the processing of emotions.
- Alpha Waves – moderate frequency (8–12 cycles/second) Brainwaves that are most common during daydreams, meditation, and other forms of relaxed focus. They are associated with bridging conscious awareness and subconscious drives.
- Beta Waves – high frequency (12–30 cycles/second) Brainwaves that are most common during active mental engagement, such as problem-solving, decision-making, analytical thinking, and other instances of high alertness.
- Gamma Waves – very high frequency (30–100 cycles/second) Brainwaves that are involved in learning and high-level cognitive processing, likely playing a key role in connecting information across different areas of the brain. They are often seen in states of peak mental performance.
- Ephaptic Transmission (Ephaptic Coupling; Ephaptic Field Effects) (Ragnar Granit, Edgar Adrian, 1940s) – electromagnetic fields produced by neurons or axons rather than synapses
Other associated discourses and additional frequently encountered topics of discussion include:
- Genetics of Intelligence – an academic domain focused on better understanding the roles of genetics in intelligence – and, in particular, the manners in which genetics influence neural structures
- Mirror Neurons – a neuron cluster that fires when one acts, when one observes another performing that act, or when one imagines engaging in that act. There was a spike of interest in the phenomenon among educators in the early 2000s, embraced simultaneously as support for and critique of action- and experience-based teaching emphases.
- Neural Constructivism – the perspective that cognitive development involves the dynamic interaction of the neural substrate of one’s brain and one’s environment
- Neural Decoding – the attempt to retroactively interpret traces of electrical activity in the brain in terms of the receipt and interpretation of sensory information as well as the triggering of decisions and activities based that information
- Neurobiology – a field of research that combines interests in Neuroscience and physiology. In this sense, Neurobiology might be described as the complement of Psychology among discourses on learning. Whereas Psychology looks at the functions of the brain and the nervous system, Neurobiology studies their structures and dynamics. Subdiscourses include:
- Interpersonal Neurobiology (Relational Neurobiology) (Daniel Siegel, 1990s) – a perspective that integrates Neurobiology with research on the social, situated, distributed, and cultural aspects of learning and identity
Commentary
The matter of how the brain works is not the same as the matter of structuring the learning experiences of the school-aged learners. Part of the reason for that is the obvious fact that knowing about a subsystem in a complex evolving form rarely affords much insight into that grander form. Another, much more subtle part of the reason is that “knowing how the brain works” and “knowing what learning is” are not at all the same thing. Unfortunately, while much of the recent brain-focused advice for educators is well-grounded, many popular movements have arisen that try to reach too far. Neuro-Focused Discourses have contributed greatly by revealing flawed assumptions and indefensible practices. It is also demonstrating much promise in informing a range of education-related issues. But it must be engaged in conversation with – not in ignorance of – insights into learning from Psychology, Sociology, cultural studies, ecology, and other domains. On that detail, associated critical discourses include:- Neurocentrism (Sally Satel, Scott Lilienfeld; 2010s) – the reductive assumption that humans can be understood by looking principally (or exclusively) at their brains
- Digestive System – a series of organs that break down food and liquids into nutrients that the body uses for energy, growth, and repair. Poor digestive function has been associated with an array of learning difficulties and disabilities.
- Immune System – a complex network of cells, tissues, organs, and proteins that protects the body from infection and disease. A balanced immune response is seen to be crucial for effective cognitive function.
- Endocrine System – a network of glands and organs that regulate many bodily functions (including growth and development, energy level, and stress response) through the production and distribution of Hormones. While not part of the Nervous System, their overlap includes the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. Key aspects of the Endocrine System include:
- Hormone – a chemical messenger released into the bloodstream by endocrine glands. Hormones affect a wide range of physiological processes. In general, Hormones travel further distances, have a broader range of target cells, and act over longer periods of time than most Neurotransmitters, although there are some substances function as both Hormones and Neurotransmitters (e.g., Dopamine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, and Oxytocin). Hormones that are mentioned the educational literature with reasonable frequency include:
- Cortisol – a Hormone that helps manage stress by increasing blook sugar and suppressing inflammation
- Hormone – a chemical messenger released into the bloodstream by endocrine glands. Hormones affect a wide range of physiological processes. In general, Hormones travel further distances, have a broader range of target cells, and act over longer periods of time than most Neurotransmitters, although there are some substances function as both Hormones and Neurotransmitters (e.g., Dopamine, Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, and Oxytocin). Hormones that are mentioned the educational literature with reasonable frequency include:
Subdiscourses:
- Acetylcholine
- Addictive Learning
- Alpha Waves
- Amygdala
- Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
- Beta Waves
- Blood Glucose Sensing
- Brainwaves
- Central Executive Network (CEN; ECN; Executive Control Network)
- Central Nervous System
- Cerebellum
- Cerebral Cortex (Cortex)
- Cerebrum
- Chemoreception Beyond Smell and Taste
- Chronoception (Time Perception)
- Corpus Callosum (Callosal Commissure)
- Cortical Areas
- Cortisol
- Default Mode Network (DMN)
- Delta Waves
- Digestive System
- Digital Detox
- Dopamine
- Dopamine Addiction (Dopamine Dependency; Dopaminergic Addiction; Neurochemical Addiction)
- Dopamine Detox (Dopamine Fasting)
- Dorsal Vagal Complex (Primitive Vagal System)
- Electroreception
- Endocrine System
- Endorphins
- Ephaptic Transmission (Ephaptic Coupling; Ephaptic Field Effects)
- Epinephrine (Adrenaline)
- Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
- Frontal Lobes
- GABA
- Gamma Waves
- Genetics of Intelligence
- Glial Cells (Neuroglia)
- Glutamate
- Hearing (Auditory System)
- Hindbrain (Lower Brain; Rhombencephalon)
- Hippocampus
- Histamine
- Hormone
- Hypothalamus
- Immune System
- Infrared Detection (Heat Sense)
- Interneurons (Relay Neurons)
- Interpersonal Neurobiology (Relational Neurobiology)
- Left Hemisphere
- Limbic System (Emotional Brain)
- Magnetoreception
- Medulla (Medulla Oblongata)
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
- Mirror Neurons
- Motor Neurons
- Nervous System
- Nervous System Dysregulation (Dysregulated Nervous System)
- Neural Constructivism
- Neural Decoding
- Neurobiology
- Neurocentrism
- Neurons (Nerve Cells)
- Neurotransmitters
- Nociception (Pain Sense)
- Norepinephrine (Noradrenaline)
- Occipital Lobes
- Oxytocin
- Parasympathetic Nervous System
- Parasympathetic State (Rest and Digest)
- Parietal Lobes
- Peripheral Nervous System
- Pons
- Prefrontal Cortex (PFC)
- Proprioception
- Reticular Formation (Reticular Activating System)
- Right Hemisphere
- Salience Network (Salience Emotion Network; SEN; SN)
- Sensory Neurons
- Sensory System
- Serotonin
- Sight (Vision; Visual System)
- Smell (Olfactory System)
- Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
- Sympathetic Nervous System
- Sympathetic State (Hyperarousal)
- Synapses
- Taste (Gustatory System)
- Temporal Lobes
- Thalamus
- Thermoception
- Theta Waves
- Touch (Tactile System)
- Treat Brain
- Vagus Nerve
- Ventral Vagal Complex (Social Vagal System)
- Vestibular System (Balance System; Equilibrioception)
- Visceroception
Map Location
Please cite this article as:
Davis, B., & Francis, K. (2025). “Neuro-Focused Discourses” in Discourses on Learning in Education. https://learningdiscourses.com.
⇦ Back to Map
⇦ Back to List
